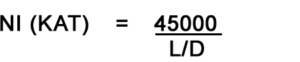Magnetic Particle Inspection of Heavy Railroad Parts
Critical to the efficiency and safety of rail systems, mechanical railroad components serve as the foundation. Rails guide the train’s trajectory, while ties or sleepers provide essential support and stability. Fasteners secure rails to ties, and ballast ensures the integrity of the track structure. Switches and crossings allow for route changes, and signals guarantee safe operations. Couplers connect railcars, while bogies with wheels and suspensions enhance ride comfort. Brake systems enable controlled deceleration, and buffers absorb impacts. Together, these components ensure smooth, secure, and reliable rail travel for both passengers and freight, highlighting the indispensable role of mechanical elements in the operation of railroad networks.
In safeguarding the integrity of railroad components, Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT) plays a crucial role. Railroads endure significant stresses, and flaws such as cracks or defects in critical parts like rails, couplers, and wheelsets can lead to catastrophic accidents. MPT, a non-destructive testing method, identifies surface and near-surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials by applying magnetic particles and subjecting the part to a magnetic field. This technique reveals issues that might go unnoticed, enabling proactive maintenance and preventing potential disasters. MPT contributes to railroad safety, ensures operational reliability, and avoids costly disruptions, emphasizing its pivotal role in maintaining the robustness of railway systems.
These parts need to be magnetized in two directions perpendicular to each other. A Circular magnetic field is generated by passing a current through the length of the part.
Calculation of head shot current is done as per the formula given in ASTM standards.
Head Shot Current = 20 X Diameter (in mm)
In the given formula, the diameter should be considered as the maximum distance between any two points along the length of the part.
A circular magnetic field is employed to identify longitudinal flaws in the part.
To detect transverse defects, a longitudinal magnetic field is generated using one or more encircling coils.
Following ASTM standards, the length of the part shaft magnetized by the coil is equal to the inside diameter of the coil.
To cover the entire length of the part, the coil must be shifted to different points along the part’s length, separated by 90% of the coil diameter. This movement ensures the 10% overlap specified in the ASTM standards.
Formula for calculation of coil current
In the above formula, the diameter should be taken as the average diameter of the part.
Additionally, in the aforementioned formula for calculating the current requirement for a coil shot, it’s crucial to note that when determining the L/D ratio, L should be equal to the inside diameter of the coil, not the overall length of the part.
For magnetic particle testing on railroad parts, a heavy-duty bench-type machine is employed. Specially designed fixtures are used to position the part on the machine. A pneumatic clamping system operates to secure the part from both ends. This pneumatic clamping ensures spark-free conditions when applying high current to the part. The use of braided copper pads is also recommended to eliminate arcing sparks.
Conventional Technique
Testing Procedure for Conventional Machines
- Clean and dry the part’s surface before inspection.
- Place the part on the fixture.
- Apply a magnetic solution bath to the part.
- Press the ‘Cycle Start’ button.
- The part automatically clamps.
- Stop the bath flow.
- Now, pass current through the part.
- Read the results on the digital metering unit.
- The part automatically de-clamps.
- Inspect the part under UV light for longitudinal defects. Rotate on steady rollers.
- Position the coil to its first position.
- Apply bath to the job again.
- Press the ‘Cycle Start’ button.
- Stop the bath flow.
- Now, pass current through the coil.
- Read the results on the digital metering unit.
- Inspect the part under UV light for transverse defects. Rotate on rollers.
- Move the coil to the next position and repeat the above 6 steps.
- Demagnetize.