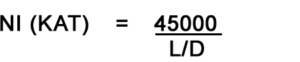Magnetic Particle Inspection of Bell housing
The bell housing in a car functions as a protective casing positioned between the engine and transmission, commonly featured in manual transmission systems. With its bell-shaped or cylindrical design, it provides accommodation for clutch components, shielding them from debris. Additionally, it serves as a connection point for the clutch release mechanism and, at times, the starter motor. This housing facilitates the proper alignment of the engine and transmission. A hole within it allows the manual transmission input shaft to connect with the engine's crankshaft, facilitating the transmission of power to the wheels. To ensure the structural integrity of the bell housing, a critical quality assessment, such as magnetic particle inspection, is conducted. This non-destructive testing method is adept at detecting surface and near-surface defects, thereby ensuring the reliability of the housing. In essence, the bell housing plays a pivotal role in safeguarding, aligning, and connecting these vital drivetrain elements. It undergoes rigorous inspections to maintain safety and performance standards in the automotive system.
The bell housing necessitates magnetization in two perpendicular directions.
To detect longitudinal flaws, a circular magnetic field is employed, generated by passing current through the bell housing’s length.
The head shot current is calculated using the ASTM standard formula:
Head Shot Current = 20 X Diameter (mm),
where the diameter refers to the base portion diameter.
For identifying transverse defects, an encircling coil produces the longitudinal magnetic field.
Formula for calculation of coil current
In the above formula, the diameter should be taken as the average diameter of the bell housing.
Magnetic particle testing on bell housings is conducted using a horizontal bench-type machine. The bell housing is positioned on the steady rollers attached to the machine’s head and tailstock. Pneumatic clamping, operated by air pressure, secures the bell housing from both ends. This method ensures spark-free conditions when subjecting the bell housing to high current. Additionally, the use of braided copper pads is advised to eliminate arcing sparks.
Conventional Technique
A two vector PLC based bench type magnetic crack detector machine is used to perform testing on the bell housings.
- Clean up and dry the bell housing’s surface before inspecting.
- Place the bell housing on the steady rollers.
- Apply a magnetic solution bath to the bell housing.
- Press the ‘Cycle Start’ button.
- The bell housing automatically gets clamped.
- Stop the flow of the bath.
- Now, the current passes through the bell housing.
- It shows up on the digital metering unit.
- The bell housing automatically gets de-clamped.
- Inspect the bell housing under UV light for longitudinal defects. Rotate on steady rollers.
- Apply the bath to the job once again.
- Press the ‘Cycle Start’ button.
- Stop the flow of the bath.
- Now the current passes through the coil.
- It shows up on the digital metering unit.
- Inspect the bell housing under UV light for transverse defects. Rotate on rollers.
- Demagnetize
Multidirectional Technique
In this tailor-made machine, the coil is automatically moved using pneumatic actuators. Since the length of the housing is short, coil is moved aside to facilitate the loading of the part.
- Ensure the bell housing’s surface is thoroughly cleaned and dried in preparation for inspection.
- Position the bell housing securely on the steady rollers.
- Apply a bath to the bell housing for optimal testing conditions.
- Initiate the testing sequence by pressing the ‘Cycle Start’ button.
- The bell housing will seamlessly be clamped, and the coil will precisely position itself.
- Halt the flow of the bath to commence the testing process.
- Allow the current to efficiently pass through the bell housing and the coil in multidirectional mode.
- Observe and analyze the results displayed on the digital metering unit.
- The bell housing will automatically undergo de-clamping after the testing is completed.
- Conduct a meticulous inspection of the bell housing under UV light, ensuring defects in all directions are thoroughly examined while rotating on rollers.